First, what is a “trailer house”?
Now, it’s no exaggeration to say that trailer houses have gained mainstream acceptance in foreign countries. There even exist areas called “trailer parks” in the U.S.
While “trailer house” is Japanese English, it is called “trailer home” in English.
Then, what is a trailer house?
A trailer house refers to what can be set up at a certain place for the purpose of settling there while employing a form of camping trailer.
Simply put, it is a house with wheels and is a so-called “movable house.”
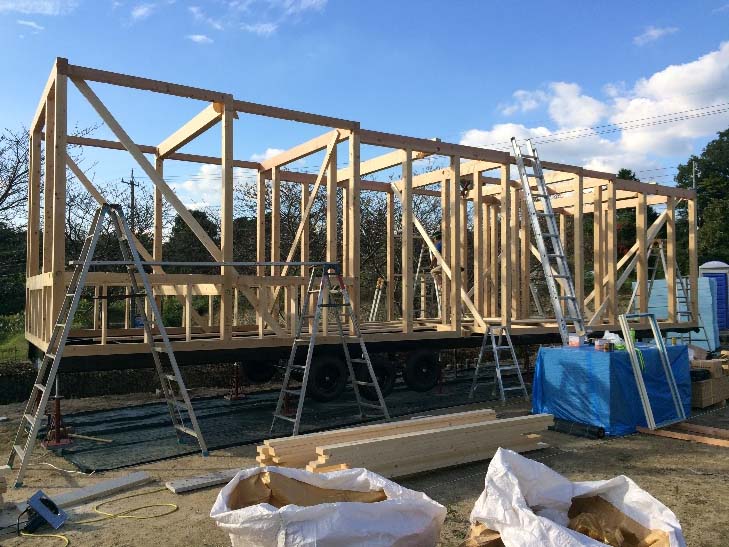

Why does BMC now offer trailer houses?
Right from the start, BMC has been running its business with the core value of creating houses with high property values.
Aside from the main residence, even if a permanent house was built for doing an extension, having a hobby room, or some other purpose, it would add an enormous debt and its asset value would hardly increase.
On the other hand, such housing would be easy to sell if it was intended for a short-term use (10 to 15 years). The rooms can be modified at will and it is easy to relocate in the future.
In case of a permanent house, it cannot be sold unless the potential customer thinks the land and the house are both worth purchasing.
In contrast, a trailer house can be set up on whatever kind of land you like as long as the location is accessible.
As such, we assume in reality the value of a trailer house can be even higher than that of a site-built home.
Why does BMC now offer trailer houses?
Until now, we have been pursuing only the minimum functions for trailer houses.
However, BMC considers that trailer houses must also possess functions tantamount to those of high-spec housing.
Although a trailer house is a temporary accommodation, it can be used not only as an extension or for a hobby purpose, but it can be extensively used in areas affected by natural disasters also.
They include being highly air tight, have high heat insulation, have a traditional conventional wooden framed structure, and are earthquake resistant.
Now that the time is ripe, we would like to be particular about trailer houses by harnessing the technologies that we have fostered to this day.
BMC considers that today we're certainly in the midst of an era when housing culture is in transition.

We are particular about the following points:
- Difference in performance from an existing trailer house
- Long-time experience accumulated in creating houses
- Our planning ability guaranteed by the achievement of constructing over 1,000 buildings
1. Difference in Performance from Existing Trailer Houses

Key Features of Floor Heat Insulation Material:
- Low heat conductivity
- Low water absorbency
- Light weight and strong
- Works well in both warm and cold weather and is capable of keeping temperatures constant

Key Features of Wall Heat Insulation Material:
- Made of high-performance glass wool—105 mm in thickness
- Heat resistance: R2.8
- Free from formaldehyde and environmentally hazardous substances

Key Features of Ceiling Heat Insulation Material:
- Made of high-performance insulation material—180 mm in thickness
- Heat resistance: R4.8
- High-performance product for the first time developed in Japan with extensively improved existing glass wool production technology
2. Long-time experience accumulated in creating houses

Traditional conventional wooden houses are suitable for Japan’s climate and natural features. Conifer wood, whose strength gradually increases after the hewing, is one of Japan’s rich resources and is also a recyclable resource.

The Japanese cypress is used for the column supports and foundation. Cypress has exceptional moist absorption and desorption property. Moreover, it has a sterilization property that natural trees typically have.

Although it is called a “trailer house,” it is possible to be used permanently in some cases. Therefore, with earthquake resistance in mind, seismic restraint brackets are installed as a standard feature to reinforce the internal structure.
3. Our planning ability guaranteed by the achievement of constructing over 1,000 buildings



Regarding our construction achievements, we have been committed to various projects, such as housing, stores, facilities, vacation houses and car dealerships. We are offering the best performance and design in view of the use, purpose and area of use. As all the houses we provide are custom made. We create them one at a time in compliance with customers’ requests through repeated meetings.
House Moving Gallery
Ugoku-HOUSE
3.5×12ver

The living room is equipped with a theater screen.
This is our original plan where you can enjoy your private space remotely from daily life. You can carry your comfortable luxurious space wherever you go. We will provide you with an exceptionally fantastic personal space in which you can make yourself at home forgetting about the time.
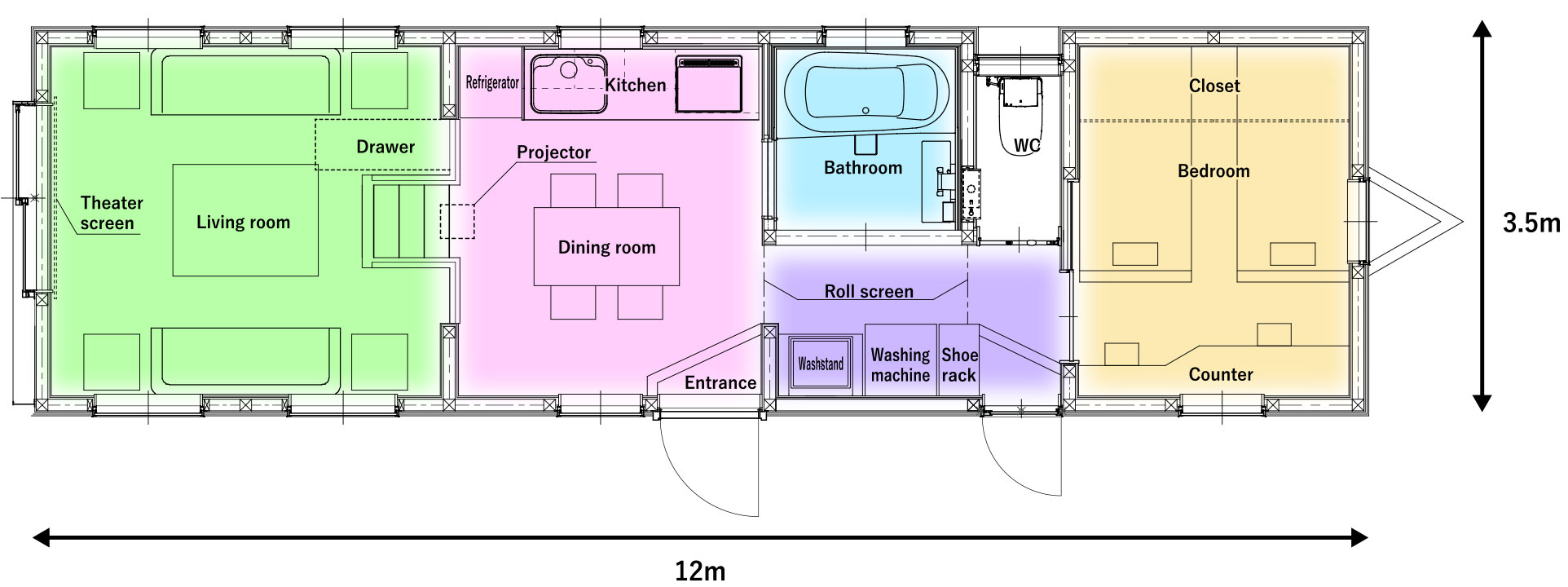
● Living room
The living room floor is outfitted with herringbone flooring adding a vintage touch. In addition, a wooden ceiling is used so that it matches in color with the flooring, forming a comfortable space.
● Dining room
There is a dining room from which you can see the modular bath through the sash window making a spacious feeling. The living room features a low room underneath, which serves also as a hidden storage space.
● Sanitary
The floor is finished with tiles best suited for a wet area giving brightness to the environment. The washstand is completely original and is capable of handling a wide variety of applications, such as a sink with a deep bowl or with a narrow one.
● Bath room
The slide entrance door with a full glass panel gives a sense of a unified space from the dressing space. Of course, roll screens and blinds have been installed to ensure complete privacy.
● Bed room
When opening the door, you can find a Japanese-style space having a completely different atmosphere from that of the entire interior space. The room has an original counter, which also serves as a study, and retractable hanging storage area, for both atmosphere and practicality.
Interior Elevation View
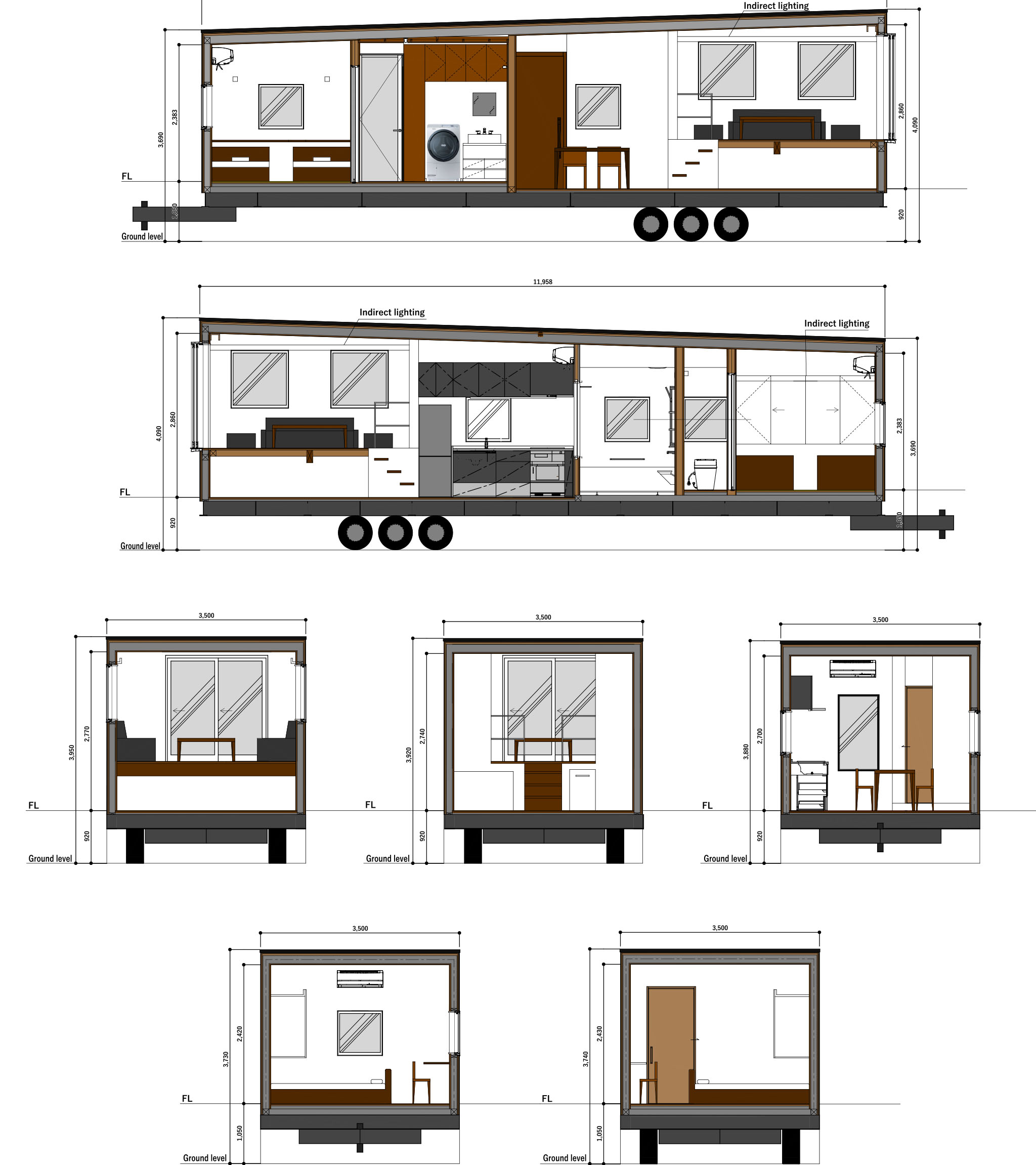
External Elevation View
Structure and Heat Insulation Material
Structure

The house body is constructed of a conventional wooden frame. The column supports and foundation are made with Japanese cypress having excellent moist absorption and desorption properties. Furthermore, cypress has a sterilization property that a natural tree typically has.
Heat Insulation Material

Thermal insulation materials that fulfill the performance of Heat-insulation Area Classification Ⅱ have been installed as a standard feature, allowing to reduce to the utmost the consumption of energy within the walls, ceilings and floors of the trailer house.
Air Tightness

After the heat-insulation work is done, airtight sheets are closely applied to ensure air tightness.
Exterior and Sash Window
Metal Siding

Metal siding has less of an impact on buildings and allows for a lightweight design.
Sash Window Performance
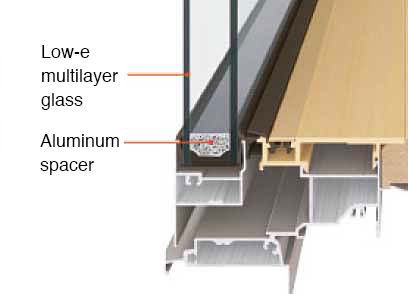
Low-e multilayer glass, capable of delivering approx. 2.0 times the insulation performance of regular multilayer glass, has been installed as a standard feature.
Design

The glass area has been expanded by 15% by miniaturizing the frame area, allowing an increase in the view and allowing in more daylight.
Interior Material
Flooring Material

The floor is outfitted with natural wood, which gives a comfortable feeling, and herringbone flooring, adding a vintage touch.
*Showroom-spec
Tiles

The wet area floor is finished with tiles—easy to maintain.
*Showroom-spec
Ceiling

The ceiling is finished with plywood, having a color tone corresponding to that of the floor, giving a spacious feeling.
Interior
Original Counter

A counter giving the image of a study is situated in the corner of the bedroom. This is our original design.
*Showroom-spec
Bedroom Ceiling

The bedroom ceiling is finished with a basswood veneer, giving a comfortable feeling.
Fittings

Natural wood finished doors have been employed in a simple and solid design in accordance with the entire style.
Facility and Equipment
Kitchen

Although a tiny space, this kitchen has a spacious feeling. This kitchen is equipped with a microwave oven.
*Showroom-spec
Modular Bath

In an integrated space from the wash area to the bathroom, this modular bath has a sufficient area--approx. 3.3 m2 in size.
*Showroom-spec
Lighting Equipment

We offer you soothing lighting which provides an experience far removed from daily life.
*Showroom-spec
Et cetera
Theater Screen

A roll-screen-type theater screen is installed.
*Showroom-spec
Wooden Blinds

Wooden blinds giving a luxurious and vintage feeling
*Showroom-spec
Projector

A ceiling mounted projector has been equipped for your precious private space.
*Showroom-spec
Enjoy Gallery
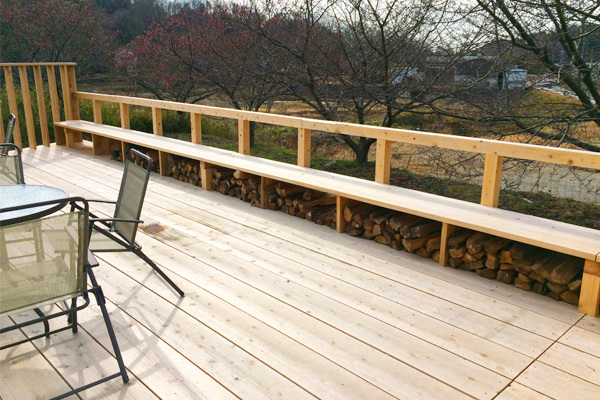
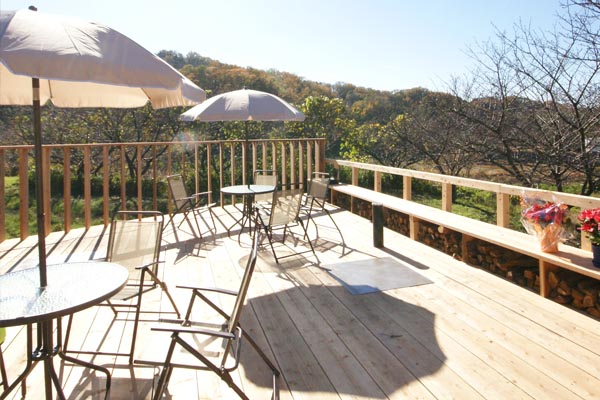
The House Moving Gallery is located at a place with a wealth of nature surrounded by mountains. A wood deck is situated between the showroom and office. On a sunny day you have a crystal-clear view. On the other hand, on a rainy day, you can enjoy a fantastic landscape produced by approaching cloud formations.
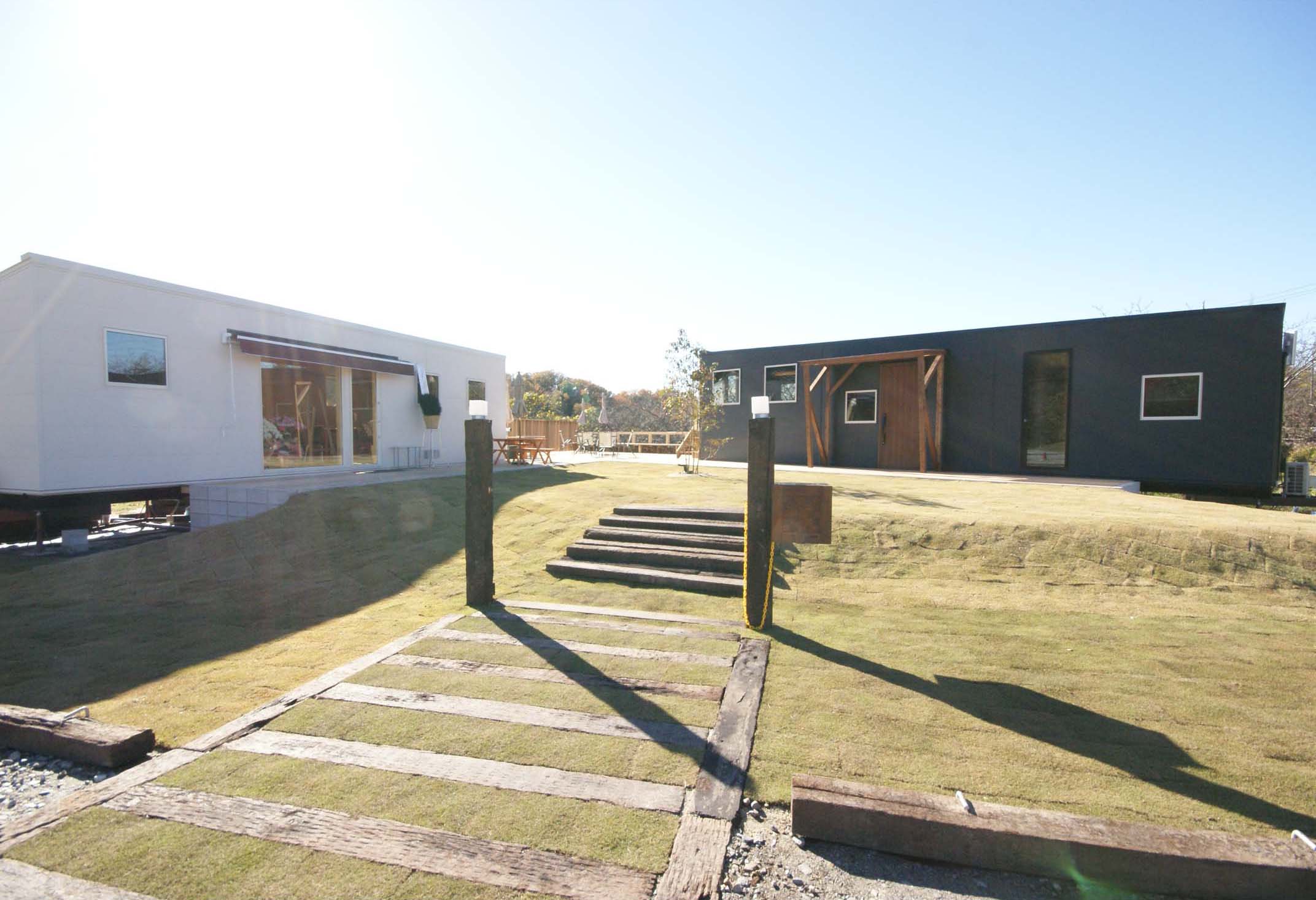

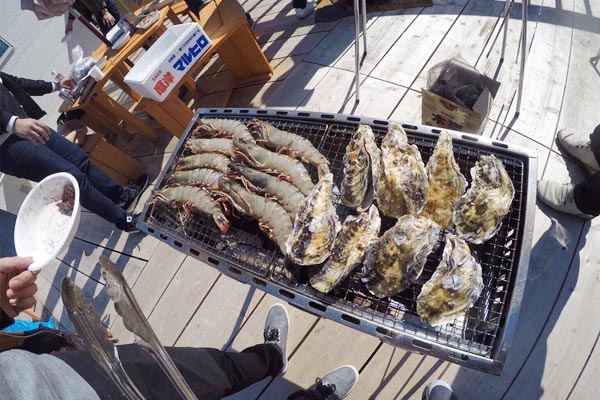
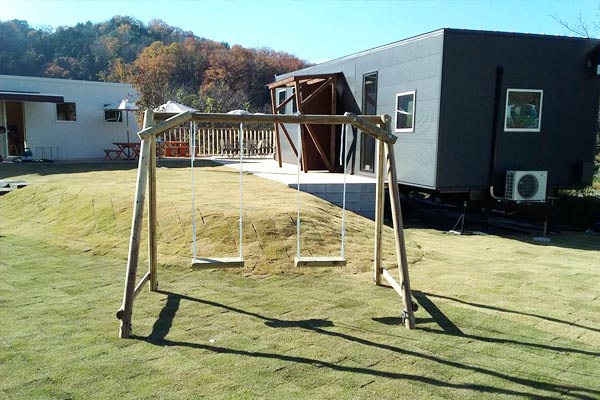
The lawn is spread all across the area. The parking area is edged with rail road ties. We’ve created a space where everyone, from kids to adults, can have a great time. With this large space full of nature, you can also enjoy a BBQ, the swimming pool, and tiny playground. For a BBQ (make a reservation in advance), you can bring food and drinks. Please feel free to visit us with your beloved family and friends.
BBQ
Note: All pictures shown are for illustration purposes only.
■ Price Plan
A table for four: 2,000 JPY/set (tax excluded)
*Please sign in at the office upon arrival.
■ We welcome your instant reviews on social media, such as Facebook and Twitter, and appreciate your feedback via our suggestion box.
《Social Media》
Post your on-site reviews of your visit to our gallery to social media: Facebook, Twitter and Instagram. In return, we will offer a fabulous bonus giveaway for the visitors who show us their posts on the spot.
《Suggestion Box》
We have a suggestion box in our office. We do appreciate your feedback and will make the best use of it as a reference for our future business.
With your cooperation, The House Moving Gallery aims to be a company that can foster great relationships and can gain extensive support from many clients.
Ugoku-OFFICE
Office2910

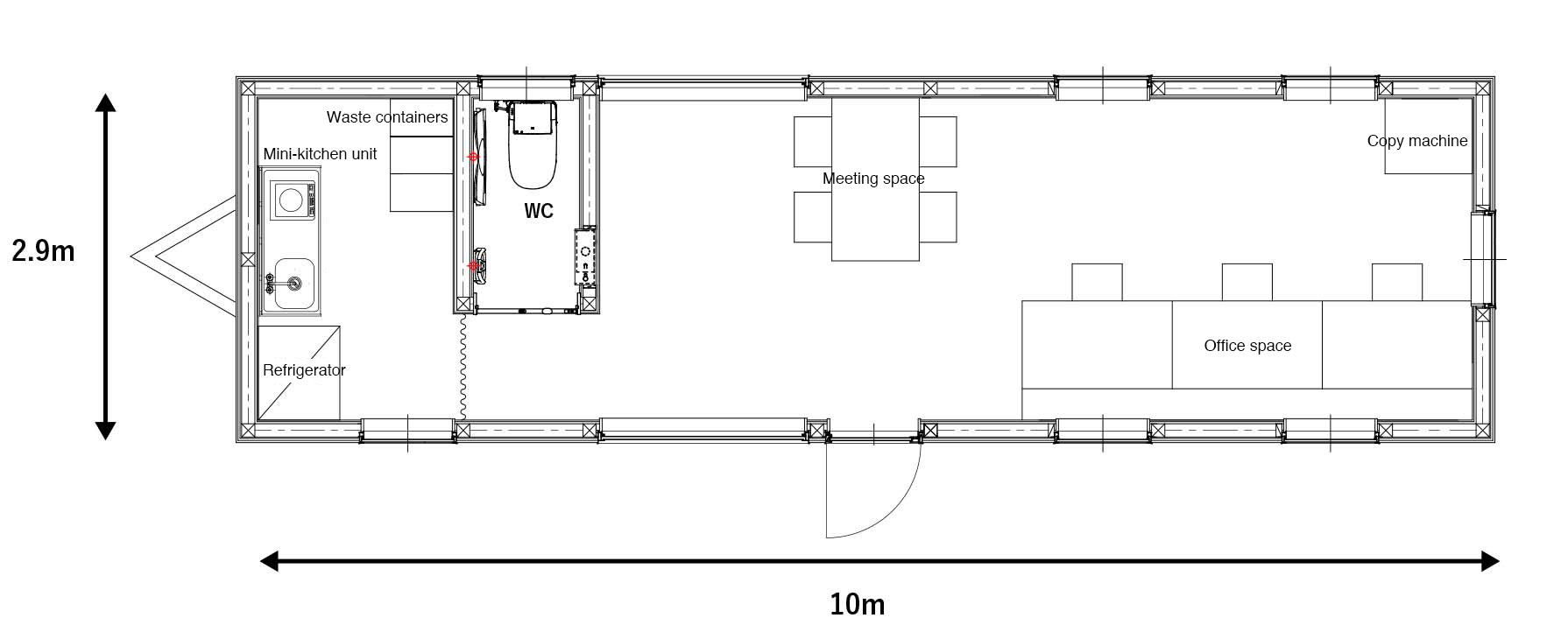
This is the main office of House Moving Gallery adjacent to the showroom. The inside walls are plywood giving a natural look. You can view the faraway mountains through the wide open sash windows located on the north and south side of the building. It is a standard box-type office building.
Structure and Heat-insulation Material
Structure

The house body is constructed in a conventional wooden frame. The column supports and foundation are made with Japanese cypress having excellent moist absorption and desorption properties. Furthermore, cypress has a sterilization property that natural trees typically have.
Heat-Insulation Material

Thermal insulation materials that fulfill the performance of Heat-insulation Area Classification Ⅱ have been installed as a standard feature, allowing to reduce to the utmost the entire consumption of energy within the walls, ceilings and floors.
Air Tightness

After the heat-insulation work is done, airtight sheets are closely applied.
Exterior and Interior
Metal Siding

Metal siding has less of an impact on buildings and allows for a lightweight design.
Interior Material

Plywood finished floors and walls having a good fit with various applications.
Lighting Equipment

This light fittings can add necessary brightness to the space and also have practical function unique to an office.
*Showroom-spec
Furniture and Facility
Mini-kitchen

The kitchen unit compactly integrates the minimum necessary hot water supply equipment.
Toilet

Despite looking compact, the toilet room has a hidden storage space behind the mirror.
Baby Changing Table (aka. Baby Seat in Japan) and Baby Chair

A child-friendly baby changing table and baby chair have been installed.
*Showroom-spec
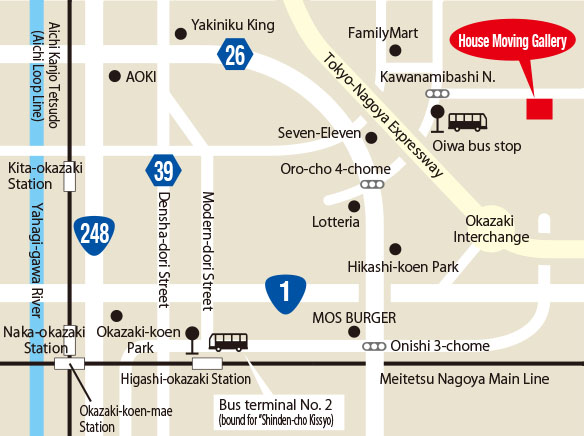
MAP
Access by Car
■ Access by General Road and Expressway
Get off at “Okazaki” interchange ⇒ Drive along National Route 26 in the north direction ⇒ Turn right at the traffic light, “Oro-cho 4-chome, 小呂町四丁目” ⇒ Turn right at the traffic light, “Kawanamibashi N., 川南橋北” ⇒ Turn right at an intersection ca. 350 m ahead
Access by Public Transportation
■ Access by Train and Bus
Get off the train at Higashi Okazaki Station on the “Meitetsu, 名鉄” line.
Take a bus bound for “Shinden-cho Kissyo, 真伝町吉祥” that departs from bus terminal No. 2 at the north exit of Higashi Okazaki Station
Get off the bus at “Oiwa, 大岩” bus stop ⇒ Walk straight along the street in the north-east direction for ca. 10 minutes ⇒ Turn right at the traffic light, “Kawanamibashi N., 川南橋北“ ⇒ Walk for 10 minutes
*Alternatively we can arrange a courtesy vehicle for you from Higashi Okazaki Station, Meitetsu line. Feel free to contact us for further details.
ADRESS

Opening Time: 10:00 A.M. to 6:00 P.M.
Regular Holiday: Monday
*House Moving Gallery is run by BMC Co. Ltd.
BMC Co. Ltd.: www.bmc-a.com
 0120-368-904
0120-368-904E-mail:info@bmc-a.com
Please do not hesitate to contact us for any inquiries about a showroom tour, the trailer house, BBQ or any other facility use.
Although we have an existing original product lineup, we also deal with full order products. Feel free to contact us for further details.
*We can receive orders from all across the country, a few exceptions may apply.
Ugoku-House

Type: Walnut
This trailer house has a size of 3.5 m × 12 m—the maximum possible size for a trailer house. It showcases walnut-colored floors and ceilings finished with plywood, giving a relaxed atmosphere.
Despite having a compact-style body, it features a spacious and active interior and is a luxurious residence-type trailer house.
It makes the best use of the space with a sense of fun. This is a completely original box-type trailer house where you can make yourself at home forgetting about the time.
Ugoku-OFFICE

Type: office 2910
This trailer house has a size of 2.9 m × 10 m—one of the most compact of its kind. Although called "compact," it features its two wide-open sash windows and a bright and spacious design.
Inside the trailer house, the floors, walls and ceilings are finished with plywood giving a simple and natural look. As there are no partitioning walls inside, it is flexible enough to meet whatever use is needed. It is an easy-to-use standard box type trailer house.
1.What is a “trailer house”?
A “trailer house” is a coined term in Japanese.
It is formally called “trailer home” in English.
[Various types of trailer houses]
(small)↓
- Travel trailer
- Camping trailer
- Travel trailer
- Fifth wheel trailer
- Park trailer
- Class A motorhome
- Class B motorhome
- Class C motorhome
(large)↑
Since a trailer house has wheels, there are two functions:
- It is driven on public roads, and
- it is installed at a certain location in a fixed way.
2. What kinds of laws are there about trailer houses?
Trailer House and the Building Standards Act
Once it is set up at a certain location and is connected to utilities—such as electricity, water and gas, the trailer house is subjected to the Building Standards Act. If you use a trailer house as “site-built structure” as stipulated in item (i), Article 2 of the Building Standards Act, essentially, it is necessary to dismount all the wheels, build the foundation, and apply for a building permit. In case of the use of the trailer house not as a site-built structure set forth by the act, the house must fulfill the conditions in which it does not fall under the category of “manufactured mobile structures” specified by the Japan Conference of Building Administration.“
The following are the conditions in which a trailer house does not fall into the category of “site built structures”:
- The trailer house shall be set up in a state in which it can be moved wherever at any time and in which such a state can be continuously maintained,
- The trailer house shall be connected and disconnected from the utilities at the site without the use of tools, and
- The trailer house shall be able to be lawfully driven on public roads.
Note: In cases where you set up a trailer house without applying for a building permit in advance and also the trailer house does not conform to the requirements of “non-site built structures,” the building is subjected to the Building Standards Act and is deemed to be an illegal building at that point. Furthermore, during the usage, in the event that a building falls into a situation in which it cannot be relocated to another location at any time, it is also treated as an “illegal building” at that point.
Trailer House and the Road Transport Vehicle Act
As defined in “manufactured mobile structures” by the Japan Conference of Building Administration, “Road vehicles are defined as what can be legally driven on public roads in accordance with the law.” The term “law” in this phrase corresponds to the Road Transport Vehicle Act. Article 4 of said Act prescribes that any road vehicles not registered in the vehicle file—vehicle inspection certificate—are deemed not roadworthy. In short, Article 4 prohibits a vehicle which does not pass a safety inspection from being driven on public roads. With regard to the requirements for passing a safety inspection, the Act specifies safety standards and the sizes of vehicles allowed on the roads in Japan. Article 2 of the Safety Standards especially stipulates the sizes.
Previously, the legal system pertaining to trailer houses was not developed enough; virtually, all trailer houses had been unlawfully driven on public roads. However, “The Reform of the Regulations pertaining to Owning and Operating a Trailer House“ was carried out by the Road Transport Bureau of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport in December, 2012. Since then, trailer houses have been added into the category of vehicles in which even if it is not possible to acquire vehicle inspection, the owner can gain a traffic permit of a special vehicle, by each vehicle individually receiving an administrative certification of deregulation. Following this revision to the law, from the legal point of view, “trailer houses” are classified as follows:
Classification of Trailer Houses under the Road Transport Vehicle Act
- Trailer house with a size within the limit specified by Article 2 of the Safety Standards
A trailer house up to the subsequent size is subject to a safety inspection: H 3,800 mm x W 2,500 mm x L 12,000 mm. When its being driven on public roads, it is crucial that such a trailer house meets safety standards and undergo a safety inspection in advance.
- Trailer house with a size over the limit specified by Article 2 of the Safety Standards
A trailer house exceeding said size can be driven on public roads after receiving an administrative certification of deregulation and after obtaining traffic permit of a special vehicle from the Road Bureau. Provided that the object is a road vehicle, it does not fall under the category of “site-built structures” defined by the Building Standards Act.
Note: Please take extra care that a trailer house in a size with which it is not subject to safety inspection does not fall into the category of “manufactured mobile structures” set forth by the Japan Conference of Building Administration. Please be sure to receive an administrative certification of deregulation and traffic permission of a special vehicle prior to driving it.
Trailer house and the City Planning Act
Development activities defined in the City Planning Act are for buildings stipulated in item (i), Article 2 of the Building Standards Act. Therefore, cases not categorized as “site-built structures” are not subject to this act. From a legal point of view, it may be misinterpreted that there is no problem with setting up a trailer house even in an area where buildings are not allowed. This is because, trailer houses are not treated as “site-built structures.” It is considered therefore to not be subject to The City Planning Act. However, BMC deems such an action as a circumvention of the law, since such a land has been designated as a regulated area for some reason. Other than the cases in which “a trailer house is used as a public facility” and similar other cases, BMC cannot but judge the action as a circumvention of the law. With that in mind, it will be necessary to make clear the law on these points in the future.
3. How many years will a trailer house last?
It varies by each product.
Our trailer house is constructed with such structures as light gauge steel, two-by-fours, conventional wooden frame—each of which has pros and cons. Please seek advice from BMC as we have an extensive insight into structures of trailer houses.
4. What taxes are charged on a trailer house?
A trailer house not falling under the category of “site-built structures” is exempted from fixed-property taxes levied on the land and building.
Nevertheless, there are some cases where a depreciation tax is charged depending on the policy of each local authority concerned. In addition, a trailer house subject to a safety inspection is also subject to an automobile tax, automobile weight tax and automobile acquisition tax when receiving the inspection. An automobile tax is levied on an annual basis. Automobile weight tax is charged when the safety inspection certificate is renewed.
5. Can I get a safety inspection certificate for a trailer house that I own?
Yes, it’s possible.
As answered in question 2—“What kinds of laws are there about trailer houses?,” it is possible to get a safety inspection certificate for a trailer house with a size up to the ceiling values specified in the Safety Standards, Article 2, of the Road Transport Vehicle Act, if the safety standards—such as the brake system—are compatible with those of the current automobile inspection system.
6. Is it necessary to report setting up a trailer house to the appropriate authority?
Essentially speaking, you don’t need to make a report under the Building Standards Act only if the trailer house does not fall into the category of “site-built structures.”
However, depending on the judgment by each local authority, there may exist some cases where some trailer houses are treated as “site-built structures” and some are not. Therefore, before making a purchase of trailer house, please be sure to consult your local architectural administration, which administers the installation location, or BMC in advance.
7. Is there any problem with long term use of a trailer house after it has been installed?
No, there is not. The term is not established by the current law.
That being said, if you are looking to keep a trailer house at the same location “permanently,” it should be dealt with as “site-built structure” as it is unnecessary to be a vehicle. JTHA (The General Incorporated Association of Japan Trailer House Association), of which BMC is a member, establishes the duration of use at the same location for up to 10 years. From the legal point of view, trailer houses fall under the category of “manufactured mobile structures.“ Please understand that a trailer house has limitations in time of use and be aware of inadvertent circumvention.
8. Is it possible to set up a trailer house on farm land?
It is possible, provided that your local agricultural committee accepts it. Agricultural land is dealt with under the provisions of the Agricultural Land Act.
However, thus far, such cases where trailer houses are approved have been extremely rare. Therefore, essentially speaking, please note that it would be almost impossible to set up a trailer house on agricultural land.
9. Is it possible to set up a trailer house in a fire prevention district and the like?
Under the current law, trailer houses are not subjected to the fire prevention standards unless treated as “site-built structures.”
Nevertheless, the Fire Services Act stipulates that even if an object which is in a fire prevention district is not a site-built structure, it must be treated as a fire preventive object. The object thereby is required to be of quasi-fire preventive construction. Moreover, from the viewpoint of a safety- and security-first, BMC has uniquely established fire prevention standards contingent on this use. Please consult BMC for further details.
10. Can I use a trailer house for a permanent dwelling? In addition, is it possible to obtain a resident registration for a trailer house?
Unless there is some particular reason, such as when it is used as a temporary dwelling in an emergency of earthquake or fire; as a house used on a daily basis, it is considered unnecessary for a trailer house to have wheels.
However, in case of a two/three family home where the number of family members may fluctuate, in the long run, the trailer house can be chosen as another solution rather than doing an extension and structural alteration of the building. In that case, the trailer house can be chosen as another option for the use as a two/three family home or holiday home, by using a site-built house as the main home--for which residence registration can be obtained. Until now, there have actually existed a few examples where trailer houses were enrolled as real properties. However, please be aware that it will be extremely difficult hereafter to obtain a residence registration unless there is some specific reason.
11. What if the road leading to the installation location is too narrow for a trailer house to be carried in? Is it possible to use a crane or to opt for a site-built construction in such a case?
For a site-built construction, a trailer house must be built as a site-built structure after applying for a building permit.
Following the Reform of the Regulations pertaining to Owning and Operating a Trailer House in 2012, it has been stipulated that a trailer house treated as “road vehicles” must be “one integrated unit.” A trailer house fabricated on site is not treated as “road vehicles,” since such a trailer house is not integrated with a vehicle. If built on site, it must be constructed as a site-built structure after applying for a building permit. In addition, if a crane is used during the construction process, the trailer house will be treated as a “site-built structure,” given the fact that it cannot easily be moved wherever and when needed.
12. Are there any local governments that have introduced any ordinances regulating the installation of trailer houses?
Yes, there are. For example;- Fujinomiya City in Shizuoka Prefecture, Karuizawa City in Nagano Prefecture are some examples...
Fujinomiya City in Shizuoka Prefecture has enacted a townscape ordinance designating some areas where trailer houses are not allowed. Karuizawa City in Nagano Prefecture has issued the Nature Conservation Protection Guideline. For nature conservation and landscape protection, the guideline bans a trailer house which does not fall under the category of “site-built structures” from being set up in the entire district.
Note: We can start the manufacture and installation of a trailer house only when we can determine the feasibility, given that such regulations may vary among each local government.
13. Can I join plural trailer houses together to expand the whole interior space?
Unless intended for long-term use, they would have to be built as “site-built structures.”
Theoretically speaking, such a trailer house is not treated as “site-built structure” as it can be:- connected and disconnected from utilities without requiring tools; installed in a manner in which it can be moved wherever at any time; and lawfully driven on public roads. However, it should be constructed as “site-built structure” unless for some reason it is used for a limited period.
14. Can I install sewer service from a septic tank to a trailer house?
Yes, you can use a septic tank to treat wastewater from a trailer house.
However, in case of a trailer house not treated as “site-built structures,” it is necessary to use tool-free fittings. When using a septic tank, please be sure to seek a guidance from your local environmental administration, and then bury it in accordance with the rule.
15. I learned that if it was only a trailer house, I would be able to obtain a permission for running a general motor truck transportation business out of a trailer house in urbanized control areas. Is this possible?
Yes, it’s possible.
Although a trailer house not treated as “site-built structure” can be legally set up within urbanization control areas, BMC is not haphazardly encouraging the owners to do so. We will be able to provide associate information ONLY to the customers who strictly observe compliance.
16. Can I run a restaurant in a trailer house?
Yes, you can.
You can run a restaurant out of a trailer house only if the trailer house meets the requirements mentioned in “Q2. What kinds of laws are there about trailer houses?” However, you must obtain a mobile food vendor permit, not a restaurant permit; provided that a trailer house is completely independent from utilities, such as by using a septic and sewer tank, power generator and the like.
17. Can I run an accommodation business, i.e. hotel, ryokan (Japanese-style hotel) and the like, by arranging plural trailer houses in rows?
If you plan to run a hotel, please consult with BMC beforehand.
Gaining a hotel business permit under the Hotel and Ryokan Management Law for running a hotel using trailer houses entails approvals from:- (1) architectural administration; (2) fire department; and (3) public health center, each of which holds jurisdiction over the installation location.
To obtain the permit, follow the steps below in numerical order:
(1) Consult your local architectural administration for the types of trailer houses that do not fall under the category of “site-built structures” and for the installation method, to make clear that the trailer house that you will own is not treated as a “site-built structure,”
(2) Consult your local fire department for the fire prevention standards and for the safety responsibilities associated with running a hotel business, and
(3) Consult your local public health center about applying for a permit for running a hotel/ryokan.
If you plan to run a hotel, please consult with BMC beforehand.
18. I learned that in case of driving with a large-size trailer house, a traffic permit of a special vehicle is needed. How can I obtain it or apply for it?
Please consult the technical support division in each local transport bureau or BMC.
In case of getting a traffic permit of a special vehicle for a trailer house, it is necessary in advance to receive an administrative certificate of deregulation from transport bureau. In addition, you must obtain both an administrative certification of deregulation and a traffic permit of a special vehicle for each vehicle prior to driving on public roads. First of all, seek guidance from the technical support division of the transport bureau that administers the installation location for applying for an administrative certification of deregulation. All the necessary pieces of information are:- size of the trailer house along with its performance, the purpose of use of the trailer house in the installation location; and owner’s background. Please consult with the technical support division in each local transport bureau or with BMC for further details.
19. Are there any penalties for driving with a trailer house on public roads without obtaining a safety inspection and/or traffic permission of a special vehicle?
Driving with a trailer house without a safety inspection on public roads is subjected to an arrest.
A person who drives with a trailer house on public roads without obtaining a traffic permission of a special vehicle and/or who drives with a trailer house past the due date of said permission is subjected to an administrative measure. Even if the owner has received traffic permission of a special vehicle, a trailer house with a width over 3 m cannot enter expressways. If an expressway is entered without permission, he/she would be arrested.
| Trade Name: | BMC Co. Ltd. |
| Capital: | 40,000,000 JPY |
| Type of Business: | Design, execution, management and contracting business of construction |
| Execution and contracting business of construction work (including its auxiliary works) | |
| Manufacturing, sales and import of furniture | |
| Design, manufacturing and sales (including used items) of trailer house | |
| Head Office: | 1-1 Nishigoihara, Hora Cho, Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture, 444-0008, Japan |
| BMC Trailer House Division: | 46-84 Kawakita, Hakoyanagi Cho, Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture, 444-0001, Japan |
| Toll-free: | 0120-368-904 |
| Phone: 0564-64-0067 Fax: 0564-64-0069 | |
| Representative: | President, Toru Aoyama |
| Founded: | November 4, 2014 |
| Business license: | Aichi Prefectural License for Specified Construction Business (Specified-26) No. 64978 |
| Antique Trading License No. 543851605000 |








 MAP
MAP